Operators ask one pressing question. How do EMD aftercoolers raise locomotive engine performance and reliability? The short answer is cooler, denser intake air. That unlocks horsepower, fuel efficiency, and lower emission. Pain points include heat soak, fouling, and inconsistent cooling system control. Use these actions to stabilize performance fast.
- Inspect aftercoolers for fouling every 1,000 hours
- Monitor intake air temperature in real time
- Balance the locomotive radiator and oil cooler flows
- Pressure test the heat exchanger core quarterly
- Verify thermal conductivity with calibrated probes
- Flush coolant to restore engine cooling capacity
- Check engine oil contamination sources
- Upgrade your EMD aftercoolers when delta-T drops
- Stock critical locomotive parts for fast swaps
- Partner with Mikura International for export-grade spares
| Action | Frequency/Trigger |
|---|---|
| Inspect aftercoolers for fouling | Every 1,000 hours |
| Pressure test the heat exchanger core | Quarterly |
| Upgrade EMD aftercoolers | When delta-T drops |
| Partner with Mikura International for spares | As needed |
Understanding EMD Aftercoolers
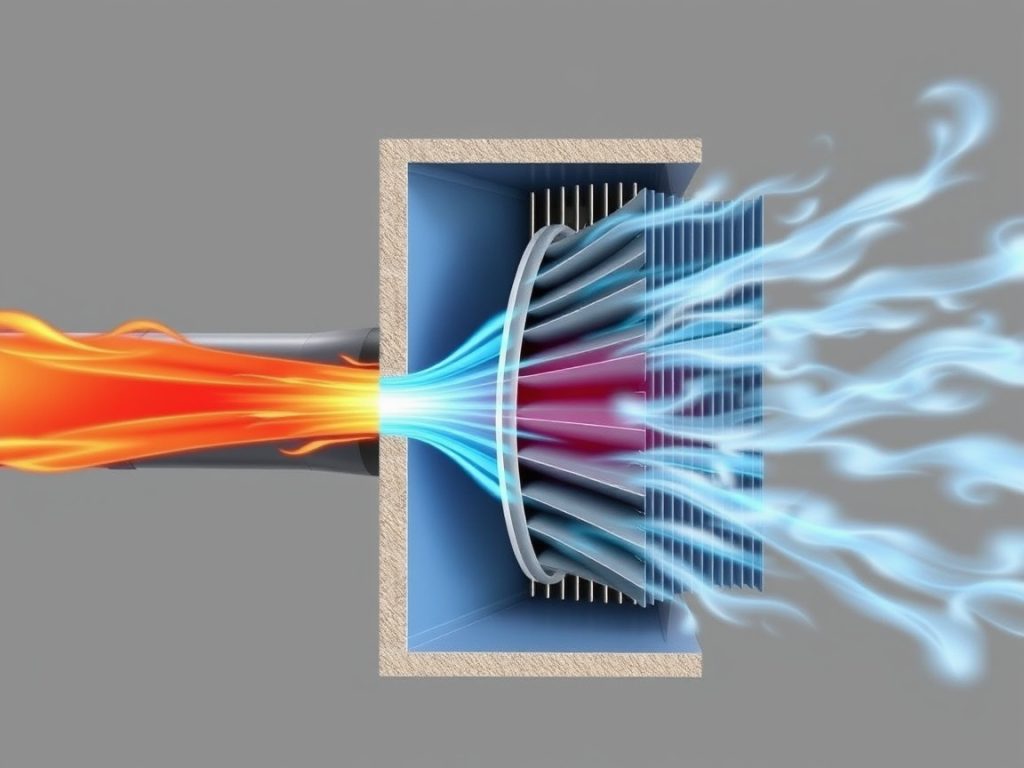
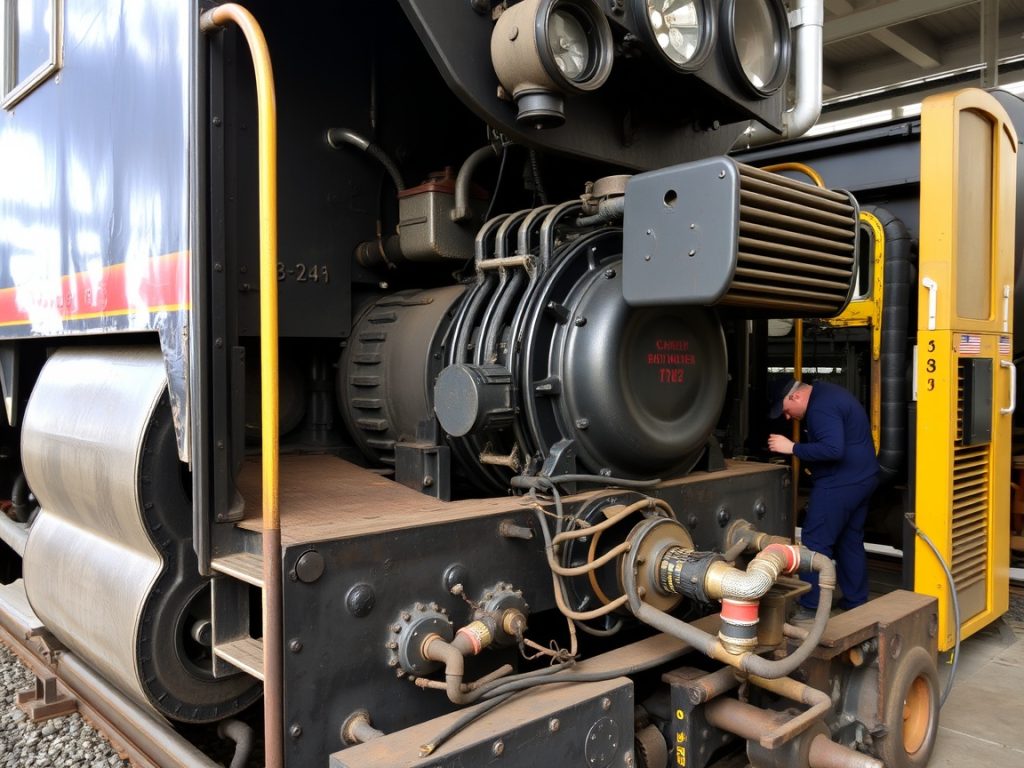
EMD aftercoolers are specialized heat exchanger assemblies that cool compressed intake air before combustion in a diesel engine. In an EMD locomotive, turbocharged air heats during compression. Cooling reduces air temperature and raises density. The engine ingests more oxygen per cycle. That improves combustion, horsepower, and fuel efficiency. The aftercooler works with the radiator, oil cooler, and broader cooling system. Together they stabilize thermal loads and protect the EMD engine from knock, stress, and premature wear.
What are EMD Aftercoolers in Locomotives?
EMD aftercoolers are modular cores and headers built for high flow and rugged duty in the rail industry. They sit between the turbo and intake manifolds of EMD diesel engines, such as the EMD 710 engine. Their fin and tube geometry improves thermal conductivity and airflow. Coolant or air-to-air designs are used depending on the locomotive model. Correct sizing is vital to unlock the full potential of your EMD locomotive’s engine performance. Precision manufacturing ensures leak integrity and stable pressure drop.
Function of Aftercoolers in Diesel Locomotive Engines
The core job is to lower intake air temperature after compression. Cooler air carries more oxygen, which sharpens combustion and reduces unburned fuel. The aftercooler acts as a controlled heat exchanger linked to the locomotive radiator and engine cooling circuit. It also trims thermal stress on pistons, valves, and liners. That lowers engine oil oxidation and deposit formation. Stable intake conditions improve transient response. The result is steadier horsepower, lower specific fuel consumption, and cleaner emission under real rail loads.
Importance in Locomotive Performance
Effective EMD aftercoolers drive measurable gains across duty cycles in the world of locomotives. They raise charge density, improving torque at low rpm and sustained power at peak load. Better thermal control protects engine components and extends TBO. Fuel efficiency improves when air temperature targets hold. Emission falls due to more complete burn. A tuned aftercooler complements the locomotive radiator, oil cooler, and engine cooling strategy. Mikura International supplies export-grade assemblies and kits that restore an EMD locomotive’s cooling power and reliability under harsh climates.
Benefits of EMD Aftercoolers in Locomotives
Rail operators demand proof that EMD aftercoolers translate into real engine performance gains. The benefits are concrete: lower intake air temperature, denser charge, and controlled thermal loads. These outcomes stabilize combustion in an EMD engine across grades and climates. The right heat exchanger design elevates horsepower while trimming emission. When integrated with a healthy cooling system and locomotive radiator, aftercoolers protect engine components and reduce lifecycle costs. The result is predictable power, fewer unscheduled stops, and stronger asset utilization.
Enhanced Cooling Efficiency
EMD aftercoolers boost cooling efficiency by rapidly removing heat from compressed intake air. Lower air temperature increases oxygen density in the diesel engine, improving the burn. Superior thermal conductivity in the core reduces approach temperature to coolant. This eases stress on the radiator and oil cooler. Balanced flows stabilize the engine cooling circuit during heavy haul. Consistent delta-T across the aftercooler maintains repeatable combustion. That steadiness underpins reliable horsepower in the world of locomotives.
Reduction of Engine Wear
Cooler intake air reduces peak cylinder temperatures and pressure spikes. This protects pistons, rings, valves, and liners in EMD diesel engines. Lower thermal gradients cut distortion and micro-welding risks. Cleaner combustion curbs soot and varnish, safeguarding engine oil quality. With reduced deposit formation, bearing film stability improves. That extends TBO and defers overhauls. By stabilizing heat flow, aftercoolers act as a buffer for engine components. The locomotive engine runs smoother through load changes and harsh ambient swings.
Improved Fuel Efficiency
Dense intake air from EMD aftercoolers improves mixing and flame speed. More complete combustion reduces brake specific fuel consumption. The engine converts fuel to horsepower with fewer losses. Reduced knock tendencies allow precise timing control in an EMD locomotive. Intake temperature control also stabilizes turbo efficiency. The combined gains lower fuel burn across duty cycles. Cleaner burn trims particulate emission, supporting compliance. Over a service year, these savings compound, unlocking the full potential of your EMD locomotive’s operating budget.
How Aftercoolers Work
Aftercoolers are compact heat exchanger assemblies placed between the turbo and intake manifolds. Compressed air sheds heat as it passes through high-fin-density cores. The cooling medium is typically engine coolant routed from the locomotive radiator circuit. Flow management maintains target approach temperature while limiting pressure drop. Properly sized headers preserve even distribution. Sensors monitor intake air and coolant temperatures. When maintained, EMD aftercoolers serve as the backbone of the engine cooling strategy for stable engine performance and reliable torque.
Cooling Process Explained
Turbocharged air exits the compressor hot. It enters the aftercooler core where fins and tubes maximize surface area. Heat transfers to coolant, driven by temperature differential and thermal conductivity. The coolant carries energy to the locomotive radiator for rejection. Control valves and pumps balance flows to prevent heat soak. Resulting intake air exits cooler and denser. The EMD diesel engine ingests more oxygen per cycle, improving combustion efficiency and sustaining horsepower under continuous rail industry loads.
Integration with Locomotive Radiators
Integration hinges on matched heat loads and stable flow. The aftercooler shares coolant with the radiator and oil cooler. Proper sequencing ensures priority cooling during peak traction demand. Bypass circuits prevent overcooling in cold climates. Clean fins and correct fan performance are vital. Pressure tests verify leak integrity in the heat exchanger. When the locomotive radiator is optimized, the aftercooler maintains low intake air temperature. This synergy preserves engine cooling margins and enhances durability across gradients and ambient extremes.
Impact on Engine Oil Temperature
Cooler intake air moderates combustion temperatures, cutting heat rejection to the oil system. This eases the burden on the oil cooler and stabilizes viscosity. Lower engine oil temperature reduces oxidation, sludge, and varnish. Bearings and turbochargers benefit from stronger film integrity. Controlled heat flow decreases thermal stress cycles on engine components. In an EMD engine, this stability safeguards clearances and extends lubricant life. Oil analysis trends often show reduced wear metals when aftercoolers hold target air temperature.
Common Issues and Solutions

Even robust EMD aftercoolers face challenges in the world of locomotives. Heat soak, fouling, and coolant imbalances erode engine performance and fuel efficiency. Intake air temperature creeps up. Emission rises. Horsepower falls under load. The solution is early detection, clean flows, and correct pressure balance across the heat exchanger. Tackle root causes in the cooling system to restore stability. Use calibrated data to guide actions and upgrade your EMD hardware when limits appear.
Identifying Aftercooler Problems
Start with data. Track intake air temperature versus ambient and coolant. A rising approach temperature signals fouling or low thermal conductivity. Watch turbo outlet pressure for abnormal drop, showing core blockage. Inspect for coolant leaks at headers and tubes. Oil in the aftercooler points to compressor seal issues. Soot streaking suggests air-side contamination. Compare bank-to-bank delta-T on EMD 710 engine configurations. Use borescope checks to confirm fin clogging. Correlate findings with locomotive radiator and oil cooler health.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity
Keep the cooling system clean and balanced. Flush coolant on schedule and maintain inhibitor levels. Backflush the heat exchanger to remove scale and biofilm. Wash air-side fins with approved detergents to restore airflow. Pressure test cores during planned service windows. Verify pump output and thermostat function to stabilize engine cooling. Calibrate intake air sensors to trust readings. Align fan shrouds and louvers on the locomotive radiator. Replace gaskets and seals proactively. Document trends to unlock the full potential of your EMD locomotive’s lifecycle.
When to Replace Your Aftercooler
Replace when repair costs exceed efficiency gains. Persistent high intake air temperature after cleaning indicates core degradation. Cracked headers or recurring leaks justify new assemblies. If pressure drop remains excessive, flow channels may be collapsed. When emission margins tighten and fuel efficiency stalls, a new unit restores headroom. Consider an upgrade your EMD path when turbo maps shift after overhaul. Choose export-grade locomotive parts with verified thermal conductivity. Ensure compatibility with your EMD diesel engine and radiator circuit.
Expert Insights on Aftercoolers

Experienced rail industry technicians stress fundamentals. Keep the diesel engine’s heat exchanger surfaces clean, flows balanced, and sensors accurate. Small temperature rises compound into big fuel costs. In EMD diesel engines, stable intake air delivers predictable horsepower. Aftercoolers work best within a tuned engine cooling strategy. Pair condition-based monitoring with scheduled inspections. Specify gaskets and cores that match OEM geometry. When needed, Mikura International supports fleets with export-grade EMD aftercoolers and kits tailored for harsh climates and heavy-haul cycles.
Industry Best Practices
Adopt a data-first maintenance plan. Trend intake air temperature, coolant temperature, and delta-P across the core. Set alert thresholds for rapid response. Standardize cleaning procedures for repeatable results. Validate radiator fan performance each season. Use calibrated gauges for pressure tests. Replace corroded fasteners to maintain clamp load. Seal test after reassembly to ensure leak integrity. Train crews on recognizing heat soak symptoms. Keep a strategic stock of locomotive parts to minimize downtime during peak traffic windows.
| Action | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Trend intake air temperature, coolant temperature, and delta-P | Enable data-first monitoring and rapid response |
| Set alert thresholds | Support rapid response |
| Standardize cleaning procedures | Achieve repeatable results |
| Validate radiator fan performance each season | Ensure consistent cooling effectiveness |
| Use calibrated gauges for pressure tests | Maintain accuracy during testing |
| Replace corroded fasteners | Maintain clamp load |
| Seal test after reassembly | Ensure leak integrity |
| Train crews on heat soak symptoms | Improve issue recognition |
| Keep a strategic stock of locomotive parts | Minimize downtime during peak traffic windows |
Case Studies of EMD Locomotives
A heavy-haul EMD locomotive showed a 12°C drop in intake air after core cleaning, recovering 3% fuel efficiency. Another fleet balanced coolant flows, cutting bank-to-bank temperature spread by 8°C and stabilizing horsepower. A coastal service unit adopted quarterly pressure tests and caught early header pinholes, preventing coolant ingestion. After an upgrade your EMD initiative, one operator reduced emission smoke puffs under throttle changes. These cases show how disciplined cooling system control sustains engine performance.
Quotes from Engine Performance Specialists
“Intake air temperature is the heartbeat of an EMD engine,” notes a senior performance engineer. “If it drifts, fuel efficiency drifts with it.” A reliability lead adds, “Most aftercooler failures start as small flow imbalances.” A maintenance manager states, “Clean fins and accurate sensors beat guesswork.” From procurement, “Specify cores with proven thermal conductivity.” At Mikura International, we emphasize, “Right part, right delta-T, right now—this is how you protect the EMD locomotive’s cooling power under real rail loads.”
Mikura International’s Role
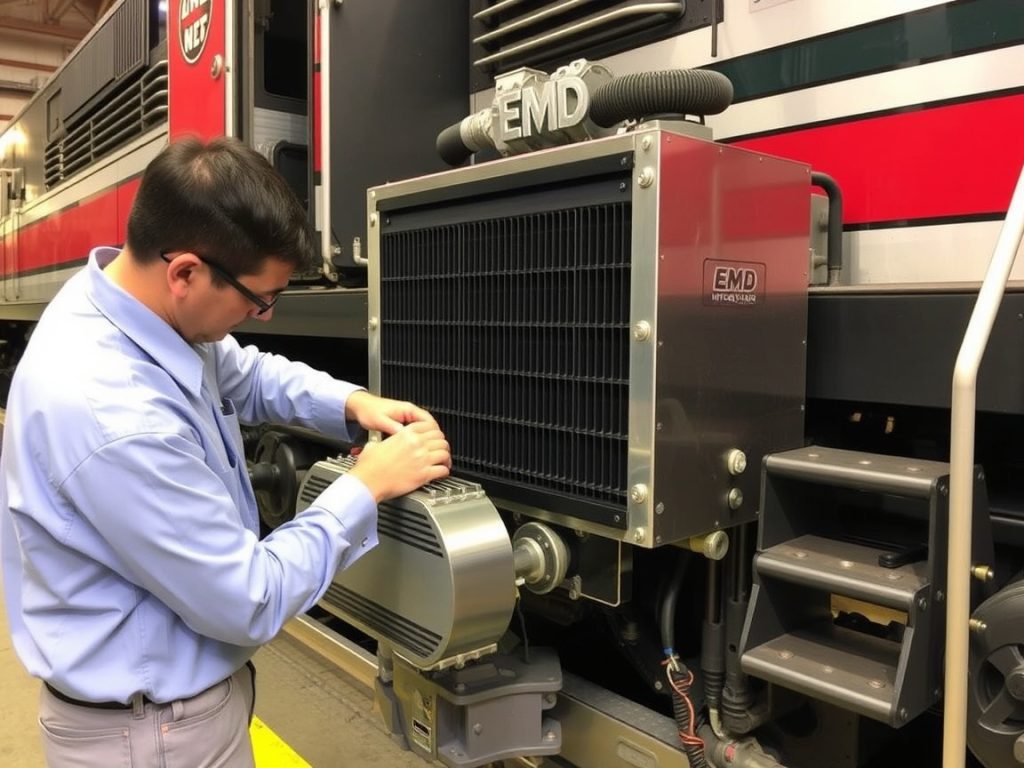

Mikura International helps rail operators fix heat, restore horsepower, and stabilize fuel efficiency in EMD locomotives. Our export-grade locomotive parts focus on EMD aftercoolers, radiator interfaces, and oil cooler integration. We validate thermal conductivity, pressure drop, and leak integrity for every heat exchanger. This ensures consistent intake air temperature and reliable engine performance. Our support includes sizing guidance for EMD 710 engine platforms and legacy EMD diesel engines. We help unlock the full potential of your EMD locomotive’s cooling system.
Quality Parts for EMD Locomotives
We source and export EMD aftercoolers engineered for high flow, rugged duty, and precise fit. Each heat exchanger core is tested for thermal conductivity and controlled delta-P. Headers, gaskets, and seals match OEM geometry for stable engine cooling. Our locomotive radiator interface kits ensure balanced flows across the cooling system. We verify braze quality and fin density for repeatable air temperature control. With proven metallurgy and inspection, our locomotive parts protect engine components, emission margins, and horsepower targets.
Commitment to Engine Performance
Our process starts with data on intake air, coolant, and ambient conditions. We align the aftercooler selection with engine cooling capacity and locomotive radiator performance. We simulate approach temperature to avoid heat soak and safeguard fuel efficiency. Every assembly is pressure tested to prevent coolant leaks into the intake air stream. We guide upgrade your EMD pathways when duty cycles change. Our goal is steady engine performance, reduced emission spikes, and reliable power in the world of locomotives.
Customer Testimonials
“Our EMD locomotive regained 4% fuel efficiency after installing Mikura International’s aftercooler,” reports a fleet engineer. “Intake air temperature dropped 10°C under peak load.” A maintenance lead notes, “Pressure-tested cores ended recurring coolant ingestion.” Another manager adds, “Balanced flow kits stabilized bank-to-bank delta-T on our EMD 710 engine.” A reliability team states, “Thermal conductivity verification protected horsepower during summer grades.” These results show the benefits of using EMD aftercoolers with proven rail industry quality.
Conclusion
Effective EMD aftercoolers transform diesel engine behavior under heavy haul. They lower intake air temperature, raise oxygen density, and stabilize combustion. That combination elevates horsepower, trims fuel efficiency losses, and cuts emission. Integrated with a healthy locomotive radiator and oil cooler, the heat exchanger preserves engine oil quality and protects engine components. With disciplined monitoring and correct sizing, operators unlock the full potential of their EMD diesel engines. The outcome is dependable power and fewer unscheduled stops.
Summary of EMD Aftercooler Benefits
EMD aftercoolers enhance engine performance by cooling compressed intake air before combustion. The cooler, denser charge improves torque and horsepower. Better thermal control reduces engine wear and emission. Stable air temperature fortifies fuel efficiency across duty cycles. When integrated with the cooling system, radiator, and oil cooler, they prevent heat soak. Verified thermal conductivity and pressure integrity maintain reliability. For EMD locomotives, these gains persist through climate swings, gradients, and sustained rail industry loads.
Final Recommendations for Locomotive Owners
Trend intake air temperature, coolant temperature, and delta-P across the aftercooler. Clean fins and flush coolant to protect thermal conductivity. Balance flows with the locomotive radiator and oil cooler circuits. Pressure test the heat exchanger during service windows. Replace cores when air temperature targets drift after cleaning. Calibrate sensors and verify fan performance. Stock critical locomotive parts for fast swaps. For export-grade EMD aftercoolers and sizing guidance, engage Mikura International to stabilize your engine cooling plan.
| Action | Purpose/When |
|---|---|
| Trend intake air temp, coolant temp, and delta-P across aftercooler | Monitor performance and detect restrictions |
| Clean fins and flush coolant | Protect thermal conductivity |
| Balance flows with radiator and oil cooler circuits | Optimize system cooling |
| Pressure test the heat exchanger | During service windows |
| Replace cores | If air temperature targets drift after cleaning |
| Calibrate sensors and verify fan performance | Ensure accurate readings and airflow |
| Stock critical locomotive parts | Enable fast swaps |
| Engage Mikura International | Export-grade EMD aftercoolers and sizing guidance |
Future of Engine Cooling Technologies
Next-generation EMD aftercoolers will feature higher fin efficiency, advanced alloys, and smarter flow control. Integrated sensors will monitor air temperature, fouling, and coolant quality in real time. Predictive models will optimize radiator and oil cooler sequencing. Coatings will resist scaling and biofilm, sustaining thermal conductivity. Modular headers will simplify maintenance in the world of locomotives. These advances will further stabilize engine performance, enhance fuel efficiency, and keep emission low under evolving rail industry demands.
FAQ
Q: How do EMD aftercoolers improve a locomotive’s performance and why is Mikura International relevant?
A: EMD aftercoolers improve a locomotive’s performance by cooling compressed air from the turbocharger before it enters the engine intake, increasing air density and combustion efficiency. Companies like Mikura International supply high-quality components and know-how that maximize the locomotive’s power and efficiency while ensuring compatibility with EMD platforms such as the EMD 645.
Q: Can you provide an accessible overview of EMD locomotive aftercoolers and explain their core function?
A: This accessible overview of EMD locomotive aftercoolers: aftercoolers act as heat exchangers that lower charge air temperature, which reduces engine intake temperatures, increases oxygen content in the intake charge, and enables more complete combustion. Mmikura International often provides retrofit and OEM-equivalent units that deliver better cooling performance and help unlock the full potential of your locomotive’s power.
Q: What are the key benefits of using EMD aftercoolers from Mikura International on older EMD 645 engines?
A: Key benefits of using EMD aftercoolers include reduced risk of detonation, improved fuel economy, increased continuous horsepower capability, and extend engine life. On EMD 645 engines specifically, a modern, high-quality aftercooler from Mikura International can reduce engine intake temperatures and restore or enhance locomotive’s performance with a high-quality upgrade.
Q: How do locomotive aftercoolers and their impact translate into measurable gains in power and efficiency?
A: Locomotive aftercoolers and their impact are measurable through lower charge-air temperatures, higher air mass flow, improved turbocharger efficiency, and reduced exhaust gas temperatures. These changes typically translate to improved fuel burn, more consistent power delivery under load, and the potential of your locomotive’s cooling system to support higher sustained output-delivering the potential of your locomotive’s power in real operating conditions.
Q: Are aftermarket upgrades from providers like Mikura International an effective upgrade that can reduce engine stress and operating costs?
A: Yes. An upgrade that can reduce engine stress and operating costs is the installation of a modern aftercooler. By reducing engine intake temperatures and improving combustion stability, these units can reduce wear, lower maintenance frequency, and improve fuel efficiency-helping to extend engine life and lower total cost of ownership.
Q: How does better cooling performance from a new aftercooler affect longevity and maintenance intervals?
A: Better cooling performance reduces thermal stress on pistons, liners, and bearings by maintaining consistent combustion temperatures and reducing peak cylinder pressures. This helps extend engine life and can lengthen intervals between major overhauls, oil changes, and component replacements-delivering long-term reliability and lower lifecycle costs for locomotives.
Q: What should fleet managers look for in an aftercooler to ensure it unlocks the full potential of your locomotive’s cooling and power systems?
A: Fleet managers should look for compatibility with the engine model (for example EMD 645), proven thermal performance, low pressure drop to preserve turbocharger behavior, corrosion-resistant materials, and supplier support for installation and testing. A high-quality aftercooler will allow the locomotive to reach the full potential of your locomotive’s cooling capacity and maximize locomotive’s power and efficiency.
Q: Is there a concise, yet accessible overview of EMD benefits and trade-offs when upgrading aftercoolers, and how does Mikura International factor in?
A: In concise terms: the key benefits of using EMD aftercoolers are improved combustion efficiency, reduced engine intake temperatures, enhanced fuel economy, and extended engine life. Trade-offs include initial upgrade cost and integration effort. Suppliers such as Mikura International can mitigate these trade-offs by offering engineered solutions that match EMD specifications, ensuring a smooth retrofit that reduces downtime and quickly realizes performance gains.


