The High Cost of Downtime: Why EMD Engine Parts Matter
Every minute your EMD 645 or 710 engine sits idle translates directly into lost revenue, missed schedules, and mounting operational costs. Whether you’re managing a locomotive fleet or maintaining marine vessels, sourcing quality replacement parts quickly becomes your most critical challenge. The struggle intensifies when you need components that match OEM specifications while avoiding counterfeit parts that could catastrophically fail under load.
Common challenges maintenance professionals face include:
- Unpredictable lead times causing extended downtime and schedule disruptions
- Quality inconsistencies between suppliers leading to premature failures
- Compatibility issues with aftermarket components
- Excessive inventory costs from overstocking to avoid stockouts
- Limited supplier transparency about parts authenticity and manufacturing standards
- Technical documentation gaps making proper installation difficult
- Rising costs from emergency sourcing and expedited shipping
- Warranty considerations when mixing OEM and aftermarket components
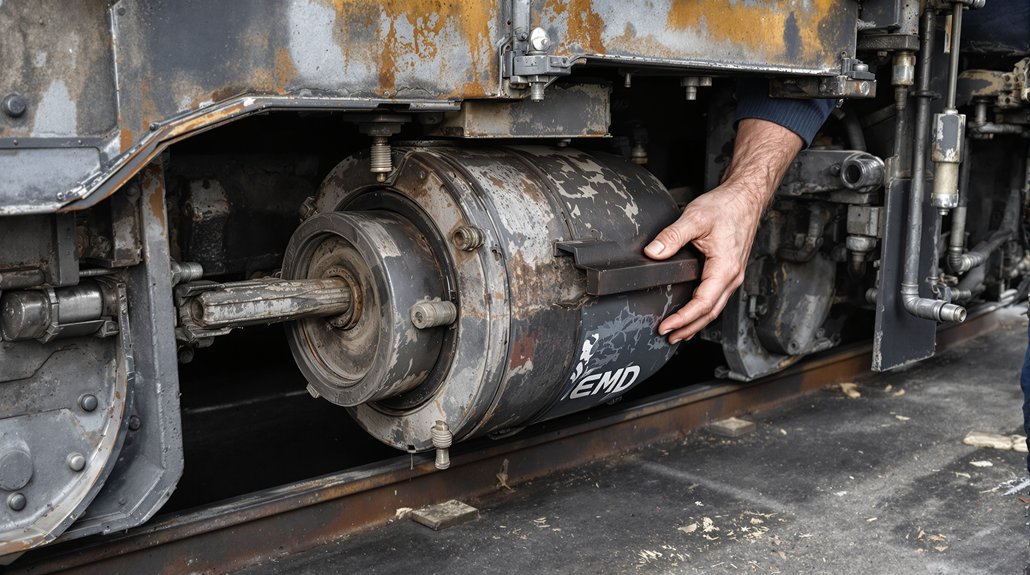
Understanding EMD 645 and 710 Engine Architecture
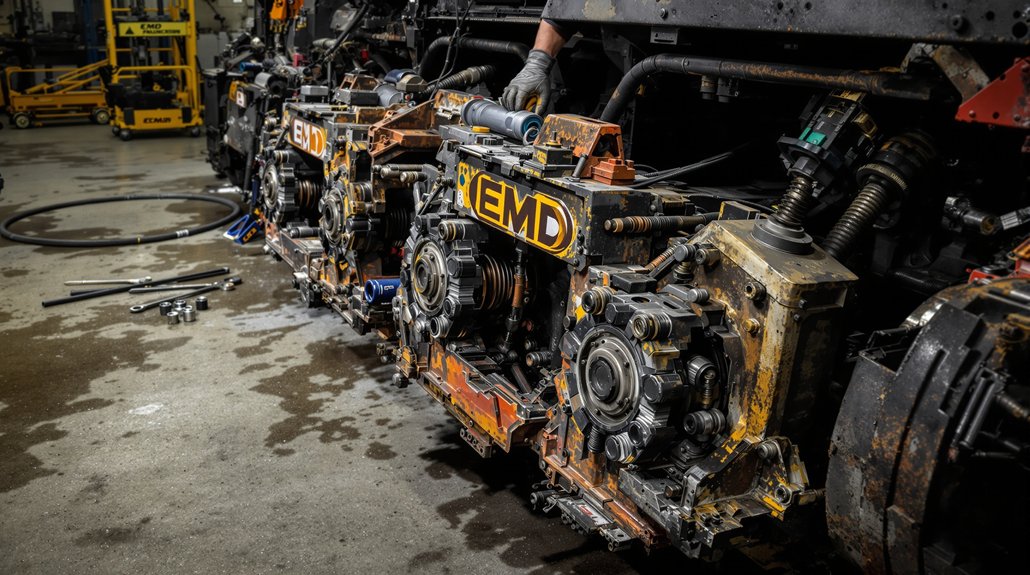
The EMD 645 and 710 series engines represent decades of proven engineering excellence in locomotive and marine applications. The 645 series, introduced in 1965, revolutionized rail transportation with its robust two-stroke diesel design, while the 710 series followed in 1984 with improved efficiency and power output. Both engines share fundamental design principles but feature distinct specifications that demand precise component matching.
These powerplants operate under extreme conditions—constant vibration, thermal cycling, and sustained high-load operation—making component quality non-negotiable. Understanding the fundamental differences between these engines helps procurement specialists make informed decisions. The 645 features a displacement of 645 cubic inches per cylinder, while the 710 increased this to 710 cubic inches, requiring larger bore diameters and modified component geometries. This distinction becomes critical when sourcing EMD 645 parts or EMD 710 parts, as interchangeability remains limited despite visual similarities.
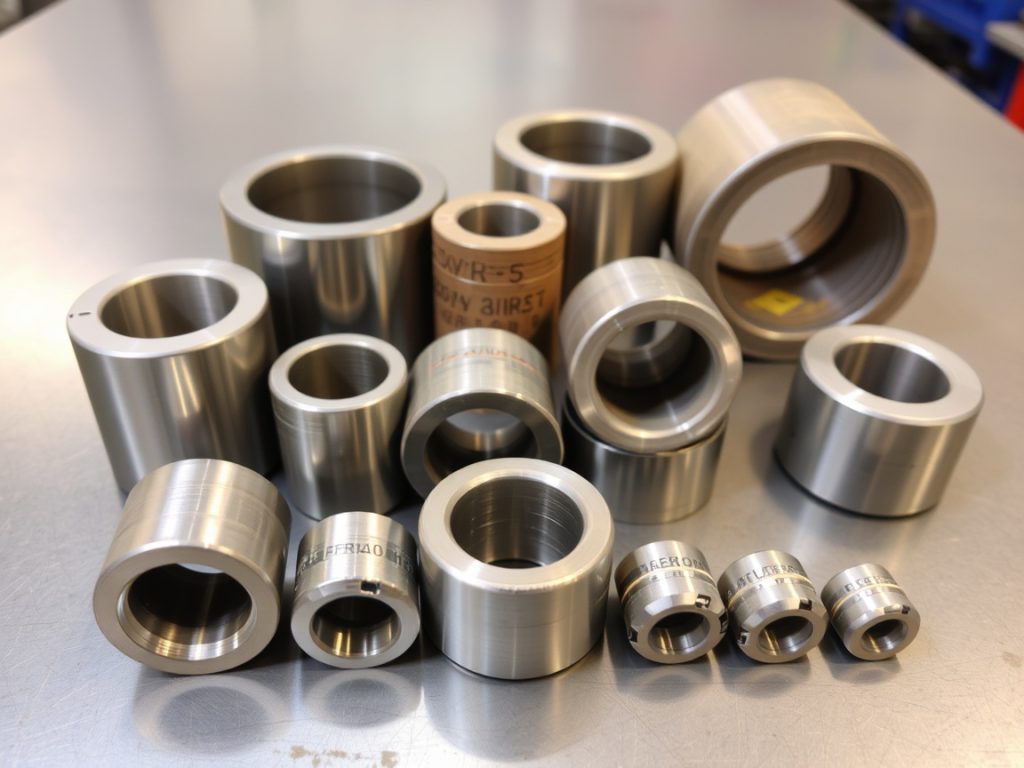
Critical Wear Components: What Fails First and Why
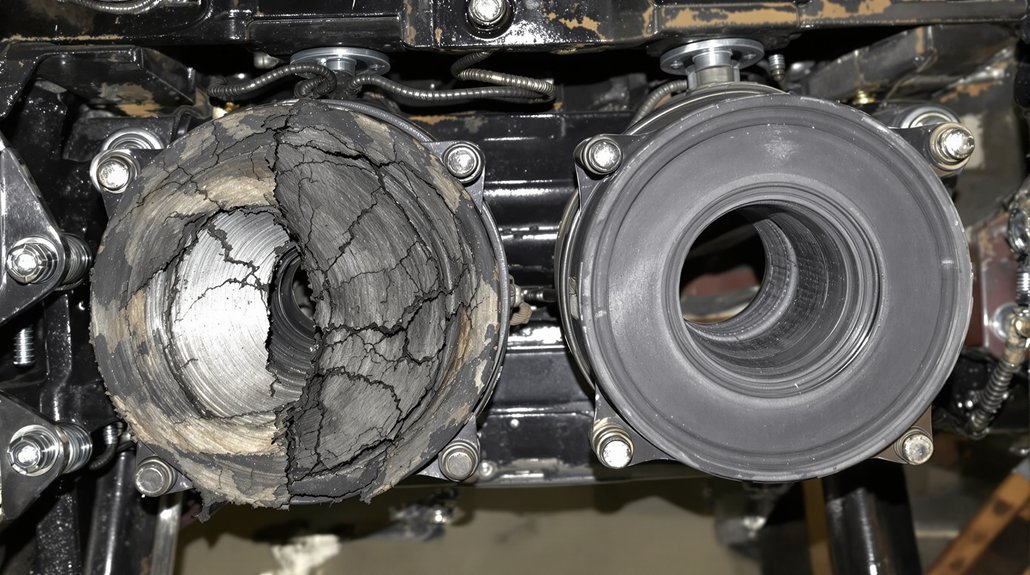
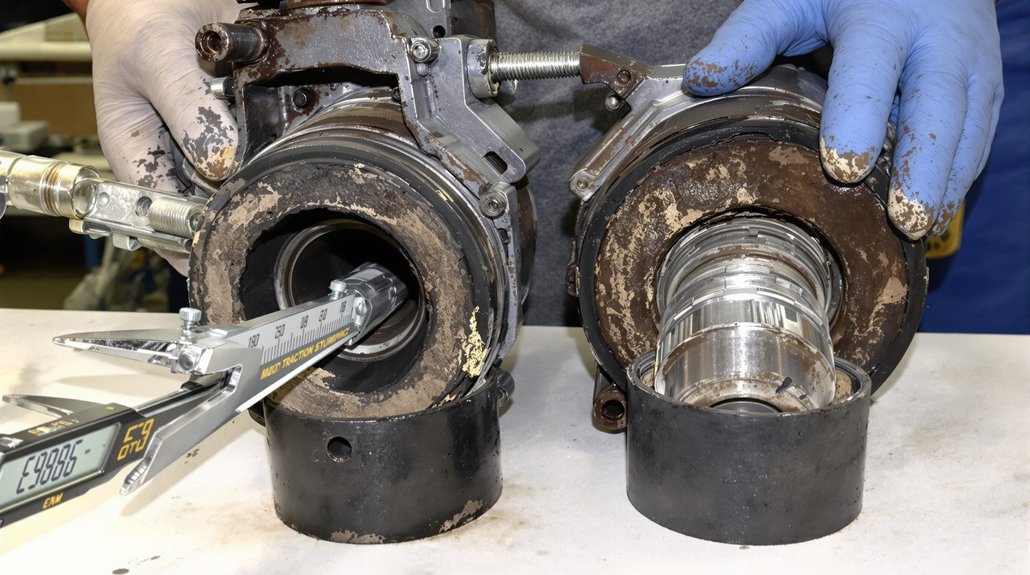
Certain components in EMD engines experience accelerated wear due to operational stresses. Cylinder liners face constant pressure from combustion forces and piston movement, gradually wearing beyond acceptable tolerances. This wear pattern manifests as increased oil consumption, reduced compression, and declining power output—symptoms every marine and locomotive engineer recognizes immediately.
Valve guides and valves themselves endure extreme temperatures and constant mechanical stress, making them among the most frequently replaced items. When exhaust valves lose their seating integrity, combustion gases escape, causing efficiency losses and potential head damage. Similarly, crankshaft bearings carry the entire engine’s rotational loads, operating in oil-film conditions that demand precise clearances. As these EMD crankshaft bearings wear, vibration increases, oil pressure drops, and catastrophic failure risk escalates. Recognizing these wear patterns allows maintenance teams to implement predictive replacement strategies rather than reactive emergency repairs.
Cylinder Heads for EMD: The Foundation of Engine Performance
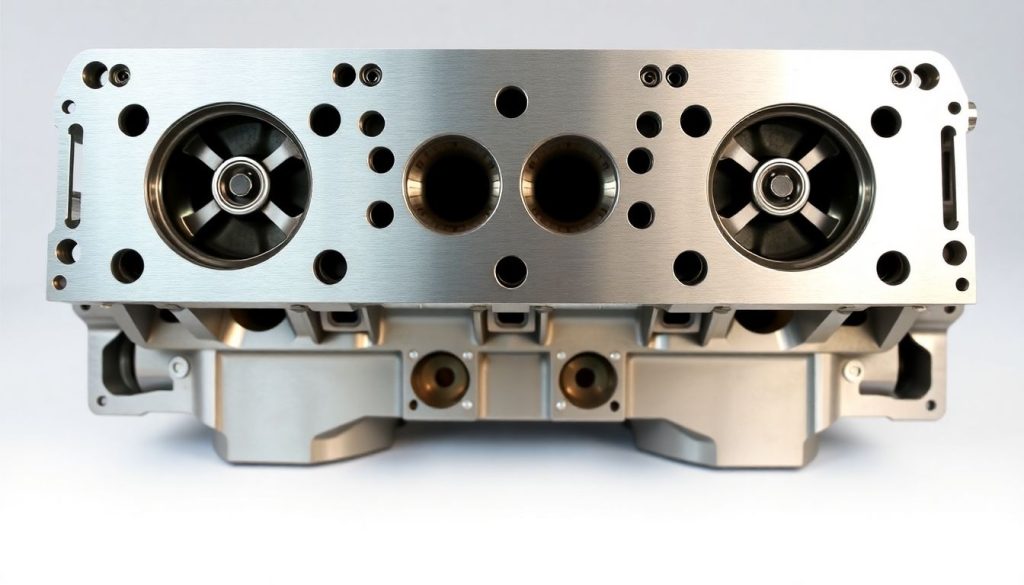

Cylinder heads represent one of the most complex and critical components in EMD 645 and 710 engines. These castings must withstand extreme thermal stress while maintaining precise valve seating, coolant passages, and combustion chamber geometry. When sourcing cylinder heads for EMD applications, specifications matter tremendously—material composition, heat treatment, and machining tolerances directly impact longevity and performance.
Quality cylinder heads feature proper metallurgy to resist thermal cracking, precisely machined valve seats that maintain compression over thousands of operating hours, and coolant passages designed for optimal heat dissipation. Inferior castings may initially appear acceptable but develop micro-cracks under thermal cycling, leading to coolant contamination of lubricating oil or loss of compression. When evaluating suppliers as an OEM locomotive parts supplier, verification of manufacturing processes and material certifications becomes essential. The best cylinder heads undergo magnetic particle inspection and pressure testing before delivery, ensuring they meet or exceed original specifications.
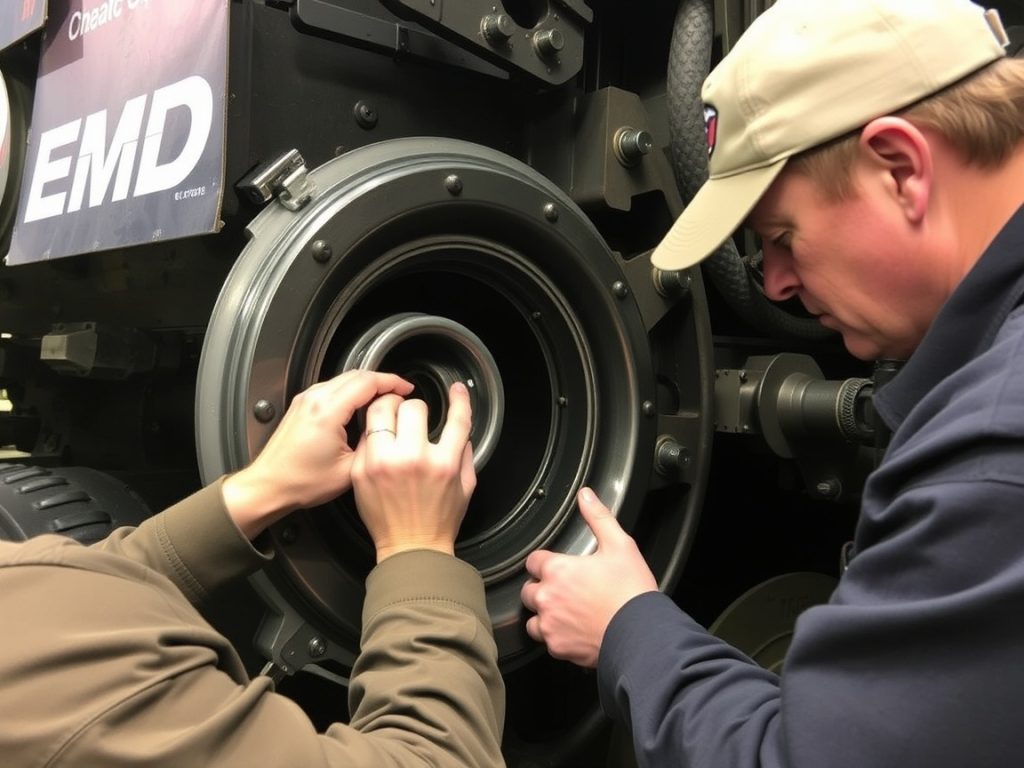
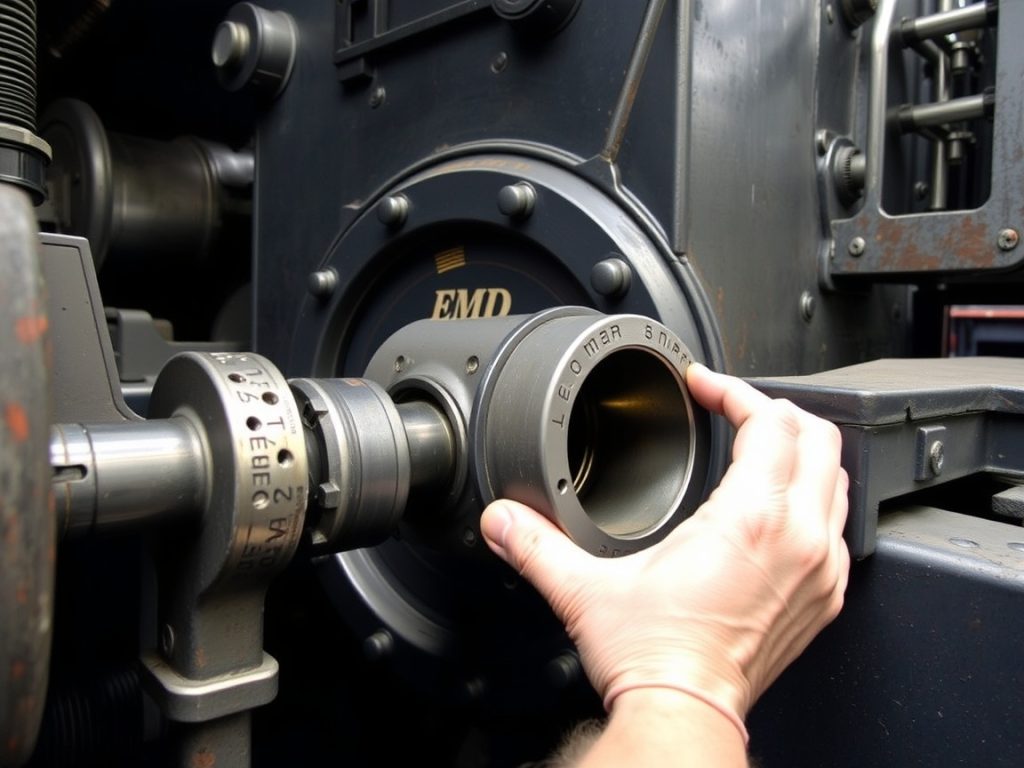
Turbocharger Systems: Maximizing Power and Efficiency
Turbochargers EMD 645 and 710 applications must deliver consistent boost pressure across varying load conditions and ambient temperatures. These precision instruments contain components spinning at extraordinary speeds—compressor wheels rotating above 100,000 RPM—requiring perfect balance and clearance control. When turbocharger performance degrades, engine response suffers, fuel consumption increases, and exhaust temperatures rise beyond acceptable limits.
Modern replacement turbochargers incorporate advanced materials and coatings that extend service life beyond original components. However, compatibility verification remains crucial—differences in housing dimensions, bearing systems, and actuator mechanisms between 645 and 710 applications prevent interchangeability. Successful turbocharger replacement requires matching compressor and turbine wheel specifications, verifying bearing clearances, and ensuring proper oil supply and return line configurations. Professional maintenance operations maintain detailed turbocharger performance logs, tracking boost pressure, exhaust temperature, and compressor efficiency to predict replacement timing and avoid unexpected failures during critical operations.
Valve Components: Precision Parts for Reliable Operation
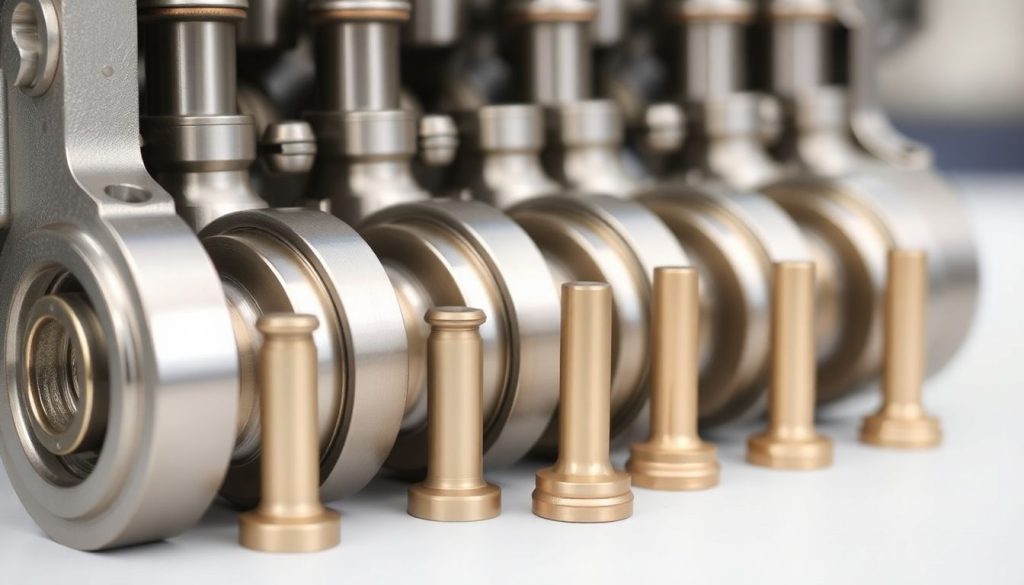

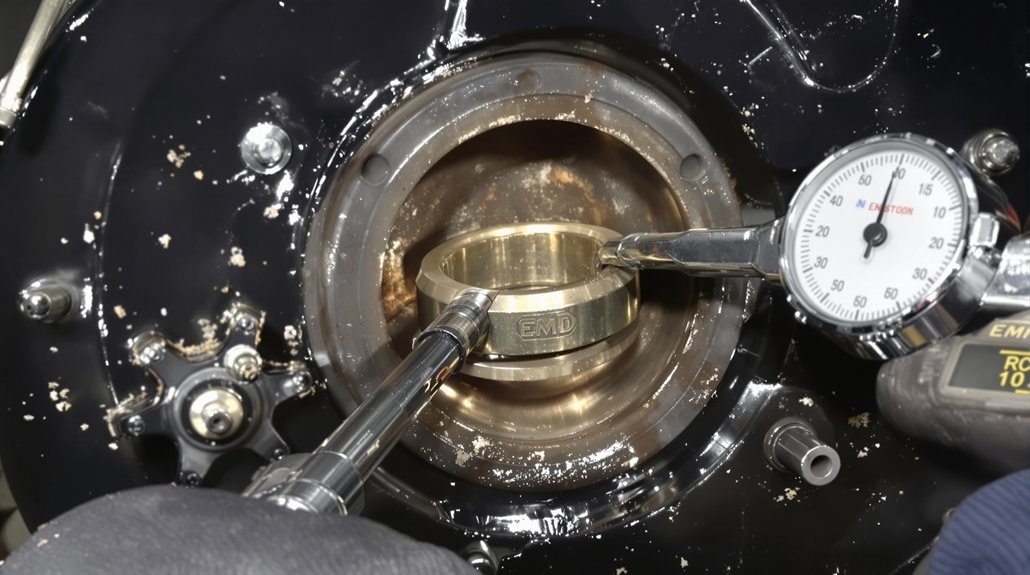
The valve train in EMD engines operates with military precision, opening and closing valves thousands of times per minute while maintaining exact timing. EMD valve guides replacement becomes necessary when valve stem clearances exceed specifications, allowing excessive lateral movement that accelerates wear on valve stems and seats. This seemingly minor issue cascades into major problems—burned valves, loss of compression, and eventual head damage.
Premium valve guides feature bronze or specialized alloy construction with precise inside diameter tolerances and proper length dimensions. Installation requires careful attention to press-fit specifications and alignment with valve seats. Similarly, valve replacement demands consideration of material composition, stem diameter, face angle, and overall length. Marine applications particularly benefit from materials resistant to sulfur corrosion from heavy fuel oils, while locomotive applications prioritize resistance to thermal fatigue. When you buy EMD engine spares, verifying these specifications prevents costly rework and ensures long-term reliability.
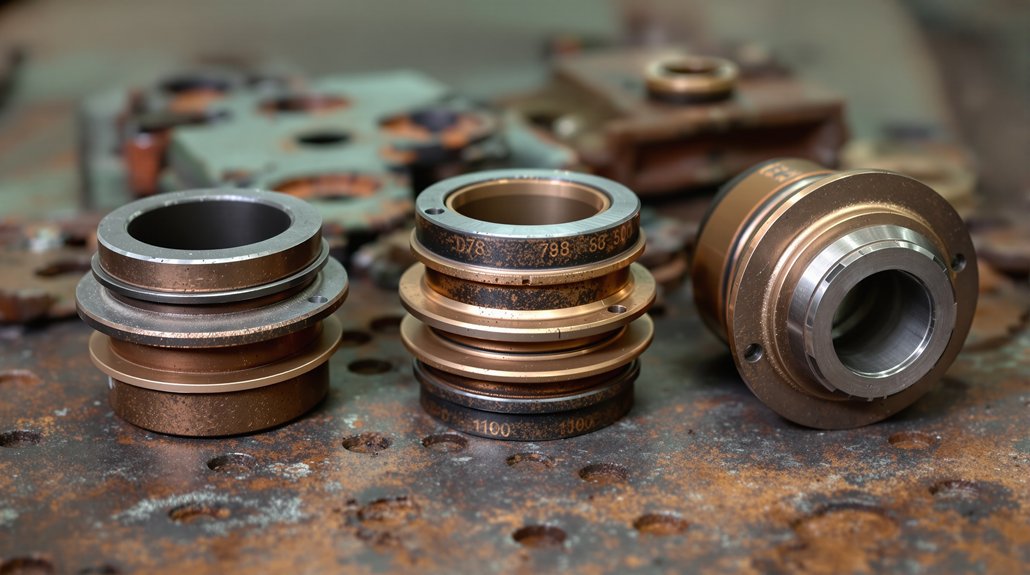
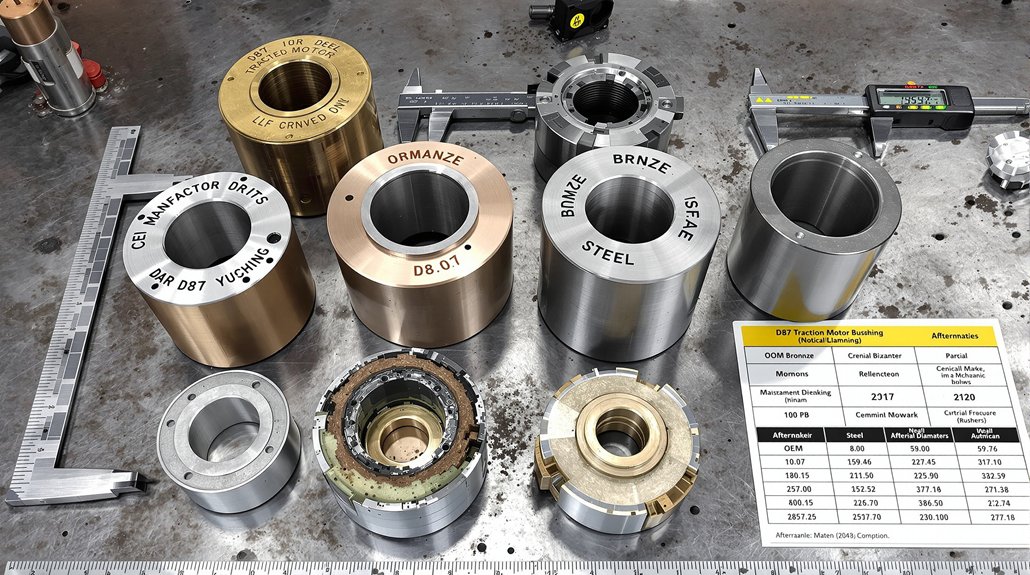
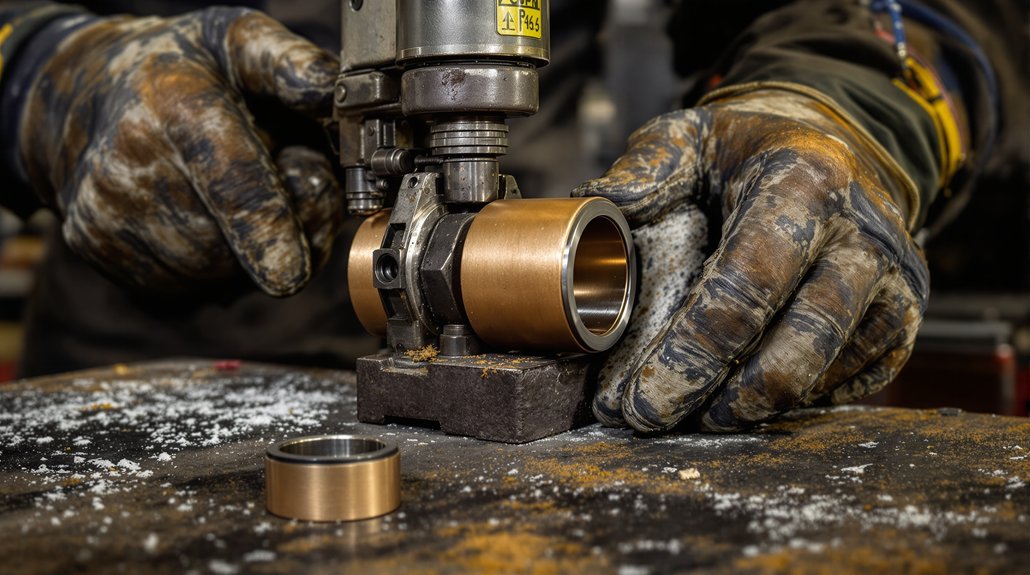
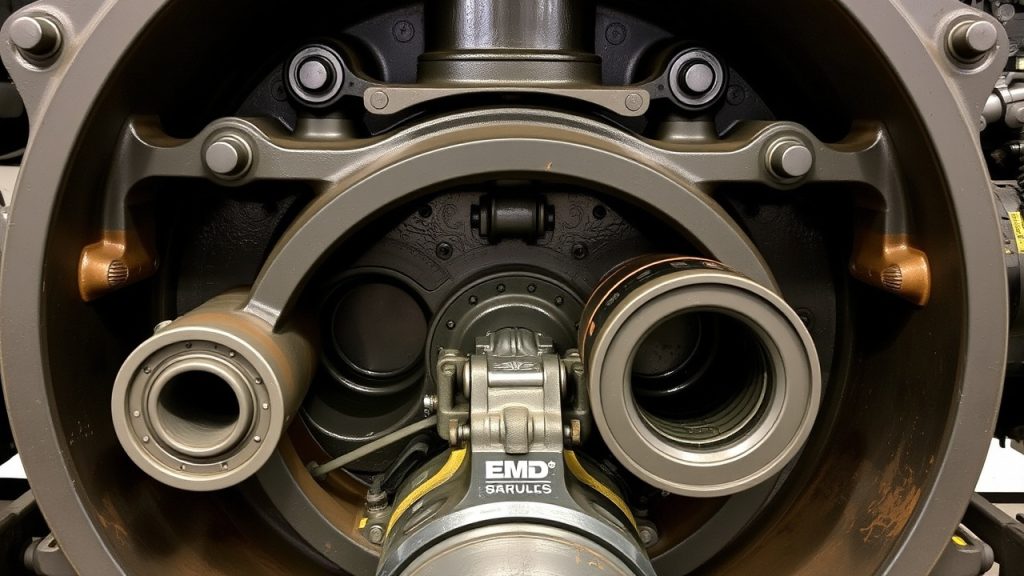
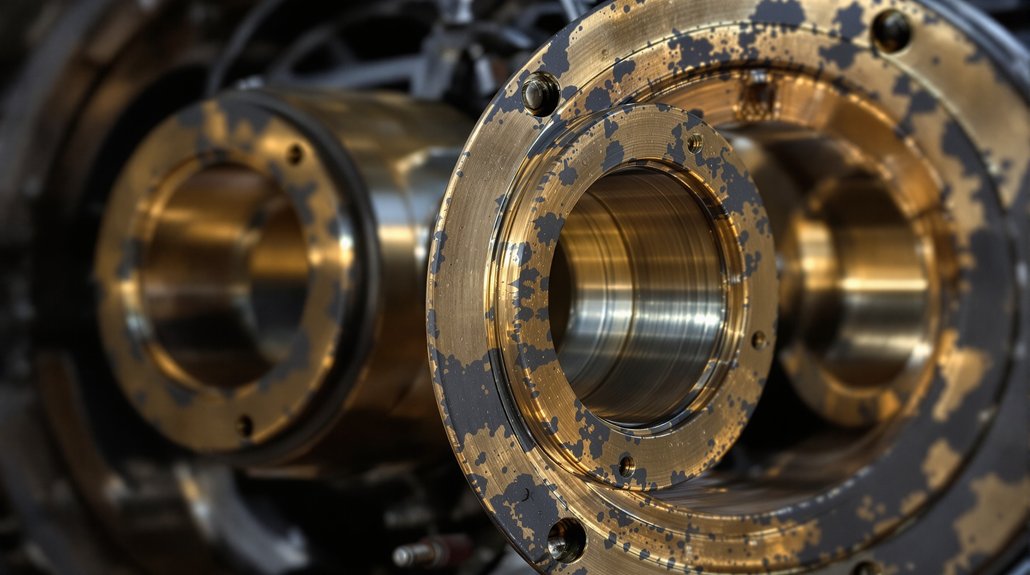
Bearing Systems: Supporting Rotating Assemblies
Crankshaft and connecting rod bearings in EMD engines operate under extreme loads while maintaining thin oil films that prevent metal-to-metal contact. These precision-manufactured components feature multiple layers—a steel backing for strength, a bronze or aluminum intermediate layer for load distribution, and a specialized overlay for conformability and seizure resistance. When bearings fail, consequences range from increased vibration to complete engine destruction.
EMD crankshaft bearings require exact thickness specifications to maintain proper clearances—too tight restricts oil flow and causes overheating, too loose allows excessive movement and triggers fatigue failures. Modern bearings often incorporate improved overlay materials that enhance resistance to contamination and extend service intervals. Procurement specialists must verify bearing dimensions, material specifications, and compatibility with specific engine serial number ranges, as EMD implemented running changes throughout production runs. Quality suppliers provide detailed cross-reference information and technical support to ensure locomotive parts compatibility across different engine variants and rebuild specifications.
Fuel System Components: Ensuring Clean, Efficient Combustion
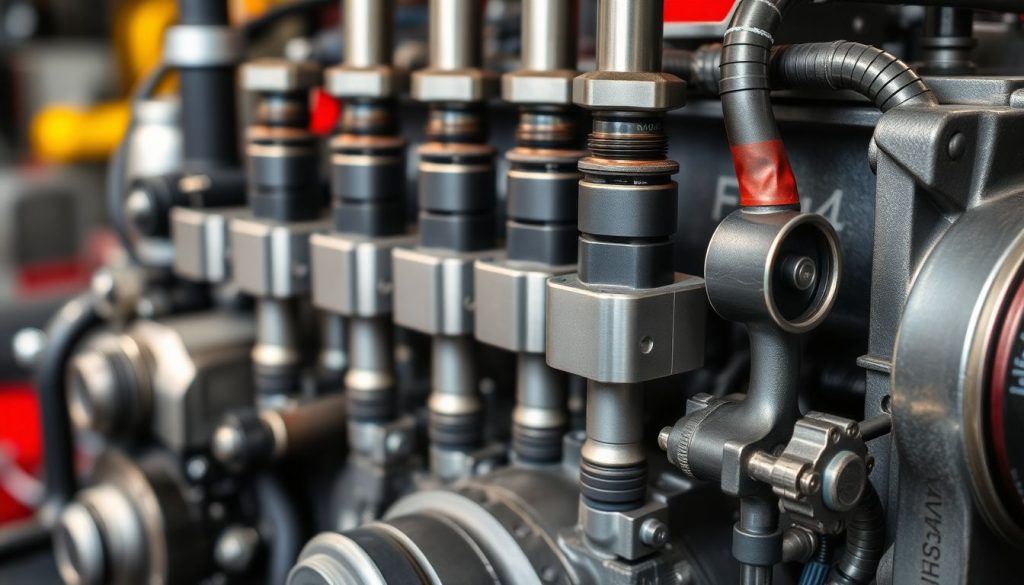

Fuel injectors and related components directly impact combustion efficiency, emissions, and power output. These precision instruments meter fuel delivery with extreme accuracy, atomizing fuel for optimal mixing with compressed air. Over time, injector nozzles wear, spray patterns degrade, and fuel delivery becomes inconsistent across cylinders, resulting in rough operation, black smoke, and reduced efficiency.
Replacement fuel system components must replicate original spray patterns, delivery pressures, and flow rates. Quality injectors undergo flow bench testing to verify performance before shipment. Additionally, fuel pumps, filters, and lines require attention during maintenance intervals. Marine applications face particular challenges from fuel quality variations and contamination, making robust filtration and regular component inspection critical. Understanding these systems helps maintenance teams schedule preventive replacements rather than reacting to failures that could sideline equipment during peak operational periods.
Cooling System Components: Managing Thermal Loads
Effective cooling system operation prevents thermal damage while maintaining optimal operating temperatures. Water pumps, thermostats, and oil coolers work together managing heat loads generated by combustion and friction. When cooling system components degrade, engine temperatures climb, leading to accelerated wear, potential head warping, and even catastrophic failure if operators don’t catch problems quickly.
Oil coolers deserve special attention because they prevent lubricating oil from breaking down under thermal stress. These heat exchangers feature internal tube bundles and baffles that maximize heat transfer efficiency. When tubes develop leaks, coolant contaminates lubricating oil—a condition requiring immediate attention to prevent bearing damage. Replacement coolers must match original heat transfer capacity and pressure drop characteristics. Similarly, water pumps require proper impeller design, seal integrity, and bearing support. Quality lubrication/oil coolers maintain precise temperature control across varying load conditions, extending oil change intervals and protecting internal components.
Exhaust System Components: Handling High-Temperature Gases
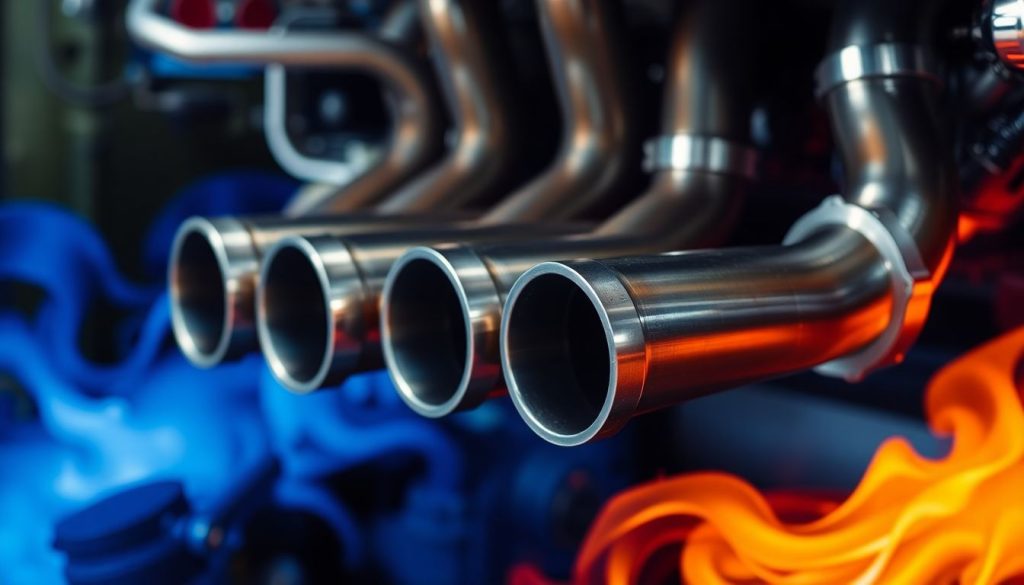

Exhaust manifolds, gaskets, and related components endure extreme thermal stress and corrosive exhaust gases. These components must resist thermal expansion while maintaining gas-tight seals that prevent exhaust leaks. When exhaust system integrity fails, consequences include reduced power, increased backpressure, and potential safety hazards from hot gas leaks.
Quality exhaust manifolds feature proper material selection and reinforcement designs that resist cracking under thermal cycling. Gaskets require specialized materials that maintain sealing ability across temperature extremes—from cold startup to full-load operation. Marine applications particularly demand corrosion resistance from sulfur compounds in exhaust gases. When selecting exhaust components, verification of material specifications and dimensional accuracy ensures long-term reliability. Professional operations maintain exhaust system inspection schedules, checking for cracks, warping, and gasket integrity before small issues become major failures.
Strategic Sourcing: Finding Reliable Parts Suppliers
Identifying trustworthy suppliers requires evaluation beyond price considerations. Quality suppliers demonstrate deep technical knowledge, maintain comprehensive inventory, and provide detailed documentation. They understand locomotive parts compatibility across different engine variants and offer technical support for complex installations. Fast delivery locomotive spares capabilities separate exceptional suppliers from mediocre ones—emergency situations demand responsive partners who maintain adequate stock levels.
Mikura International has established itself as a leading OEM locomotive parts supplier by maintaining extensive inventory of critical components and providing technical expertise that helps customers make informed decisions. When evaluating any supplier, verify their quality control processes, request material certifications, and assess their technical support capabilities. The best partnerships develop through consistent performance—reliable quality, accurate documentation, and responsive communication. Rather than sourcing from multiple vendors, consolidating purchases with proven suppliers streamlines procurement, reduces inventory complexity, and ensures consistent quality standards.
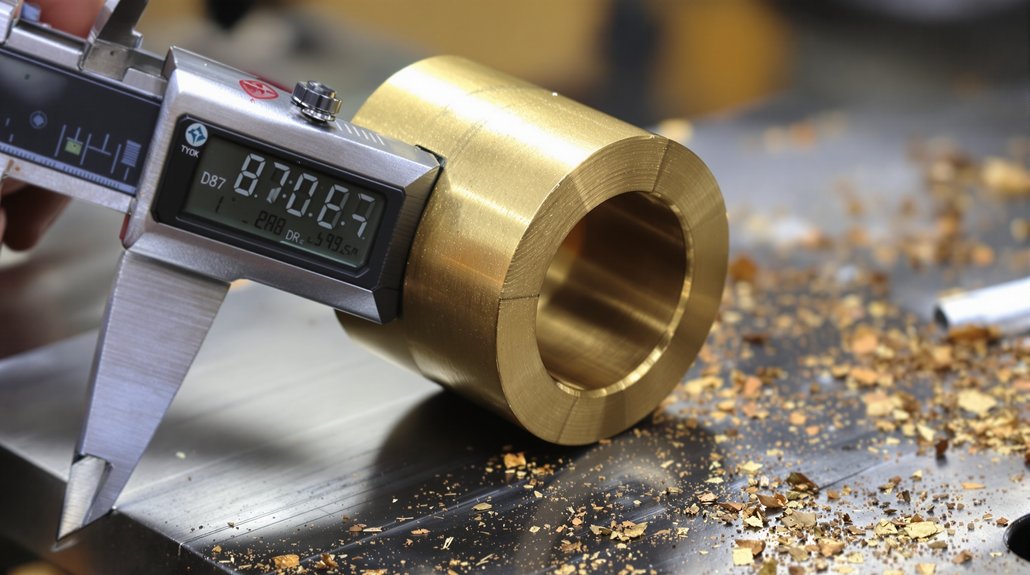
Quality Assurance: Verifying Component Authenticity
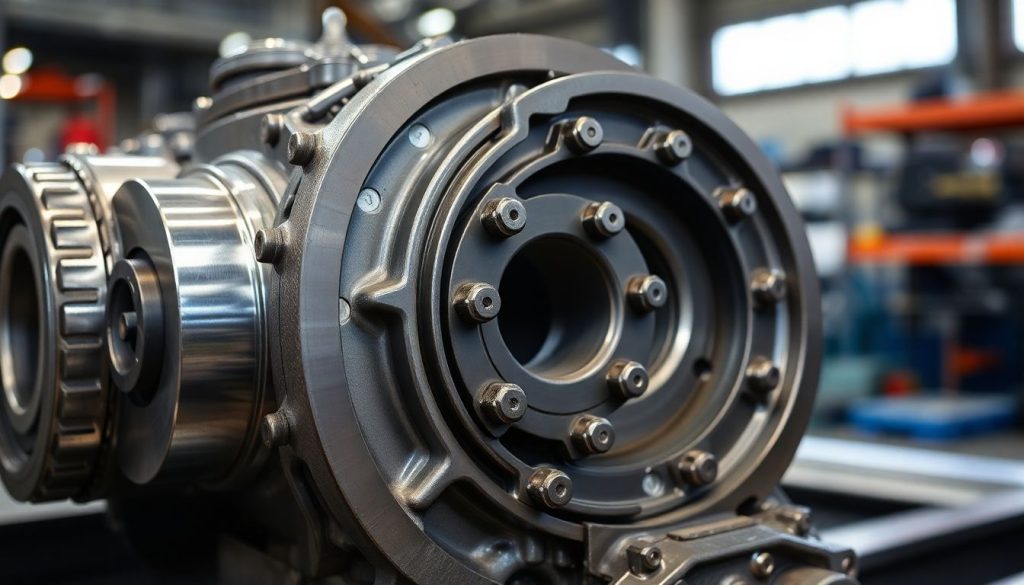

Counterfeit and substandard parts pose serious risks in locomotive and marine applications. These components may appear identical to genuine parts but fail prematurely due to inferior materials, improper heat treatment, or dimensional inaccuracies. Implementing robust quality verification processes protects against these risks while ensuring operational reliability.
Request material certifications, dimensional inspection reports, and manufacturing process documentation from suppliers. Quality components arrive with proper packaging, clear part number identification, and technical documentation. Visual inspection reveals quality—precision machining, proper surface finishes, and appropriate markings distinguish genuine components from counterfeits. When you buy EMD engine spares, insisting on documentation and verification protects your investment and prevents costly failures. Established suppliers understand these requirements and willingly provide comprehensive documentation supporting component authenticity and quality standards.
Inventory Management: Balancing Availability and Cost
Effective spare parts inventory management balances the cost of carrying inventory against downtime risks from stockouts. Critical components like cylinder heads for EMD applications, turbochargers, and bearing sets deserve priority stocking due to their long lead times and operational importance. Less critical items with shorter lead times can operate under just-in-time procurement strategies.
Computerized inventory systems track consumption patterns, predict replacement timing, and trigger reorder points automatically. Smart maintenance operations analyze historical failure data, identifying components requiring proactive replacement before failures occur. This predictive approach reduces emergency sourcing costs while minimizing downtime. Partnering with suppliers offering fast delivery locomotive spares capabilities provides additional flexibility, allowing reduced on-site inventory while maintaining quick response to unexpected failures. Regular inventory audits verify physical counts match system records, preventing surprises when critical components are needed urgently.
Conclusion: Building Reliable Supply Chains
Success in locomotive and marine engine maintenance depends on reliable access to quality spare parts. Understanding component specifications, identifying trustworthy suppliers, and implementing strategic inventory practices creates operational resilience. The EMD 645 and 710 engines deliver decades of reliable service when supported by proper maintenance and quality replacement components.
Mikura International stands ready to support your operational needs with comprehensive inventory, technical expertise, and commitment to quality. By focusing on OEM-specification components, maintaining extensive stock, and providing responsive customer service, we help maintenance professionals minimize downtime and maximize equipment reliability. The investment in quality parts and reliable supply partnerships pays dividends through reduced failures, extended component life, and improved operational efficiency.